Contd.....
- Electrical conduits shall not be run in columns.



- In soil filling as per IS code for every 100 m3 sample for core cutting test should be taken.
- Free falling of the concrete is allowed maximum 1.5 m according to IS456 is the important aspect to considered because if the drop height is more than 1.5 m segregation would happen.
- Use of stirrups is to handle the shear force and hold the reinforcement bars in position.You are aware that concrete is good at compression and steel is good at tension, thus the combination of both corners the shear force.
- Aggregate used for concrete production should be less pores, in other words it should not absorb water more than recommendation by code's, usage of such aggregate would reduce strength by absorbing water from concrete.
- Strength of concrete is inversely proportional to water cement ratio.
- Even before the construction commences, it is essential to check for certain adverse factors whose existence would necessitate the abandonment of that particular site for construction.
2. Reclaimed soils; land subject to subsidence or settlement.
3. Smoke or obnoxious odor due to vicinity to industrial areas.
- The construction site should not be a part of a land depression. The topographical conditions of a site not only determine its elevation and foundation, but also affect the lying of sewer and drains.
- The geological condition of the site are also important factors to be considered due to their effect on foundation and subsequent life and strength of the construction. If there is rocky base on the surface or below, the site is optimum as it provides and excellent base for laying the foundation and also prevents damage due to moisture.
- In northen India , longer walls are generally placed towards north & south and shorter walls toward east & west, so that minimum possible walls are exposed to the sun. The general wind direction of the site also determine the orientation of the building.
- Plinth is 60 to 75 cm above the ground level.



- Provide RCC Bands at sill, lintel, and roof levels for load bearing constructions for earthquake-resistence.
- In brick masonary some point should be noted, soak the bricks in clear water thoroughly before use. It is desirable to provide expansion joint after every 30 meter length 0f wall.
- I-section,it is very good for giving stiffness(less deformation on loading) and to withstand higher bending moments(as a result of heavy loading) on comparison with other cross-sectional shapes of same area. Also, it is very easy to manufacture. It will have more moment of inertia due to the distance of the flange from the centroidal axis and it have zero eccentricity about one axis and the center of gravity lies inside the web.
SOME IMPORTANT CONCRETE TERM
- Workability of the concrete are tested by slump test, compacting factor test, vee-bee consistometer, flow table test, kelly ball test.
- Seggregation : is define as seperating out the of the constituent parts of a concrete mix, so that the mix is no longer in a homogeneous and stable.


- Bleeding is the seperation of grout. i.e., ( cement + water ) from the mix.
- Laitence: Due to over vibration, coarse particles settles and scum rises to tops. The formations of scum is called laitence. Which causes ''Dusting Off'' of the surface; i.e., after setting of setting of concrete in powder form.
- When we make the concrete by the hand mixing usually 10% more cement should be added.
- The transit mixer (TM) should reach at the site within the 2 hour , otherwise concrete would hard within short time.
- Compacting of the concrete by the Tamping, Vibrating, Vibro-pressing, Rolling by roller, Centrifugation, High pressure and shock etc.
- Compressive of the concrete is measured by Cube testing of 150 x 150 x 150 mm cube, cured for 28 days, crushing strength determined. Grades are classified based on characteristic strength of concrete.
>>>> M25, M30, M35, M40, M45, M50, M55, M60 are the standard concrete.[ M60 is added in IS 456 , as per amendment no.4 (2013)]
- Tensile strength of concrete measure by the split tensile test.
- Modulus of rupture of the concrete is found by the using a prism od section 150 x 150 mm and 700 mm long. It is also known as a "Flexure tensile strength of concrete".
- Non Destructive Test (NDT) of concrete is tested after the concrete is in harden state. There are the various test of Non- destructive;(Acc to IS13311)
1. Schmidt rebound hammer test ( check for surface hardness )
2. Pulse velocity test or UPV test ( check the strength of concrete)
3. Concrete cover by laser based Instt.
4. Pullout Test
5. Resonance Frequency Method ( for check the frequency of specimen)
6. Pulse Echo Method ( for deep beam, to check for quality of the concrete.)
2. Retarders
3. Water reducing admixture
4. Air entraining agents
1. Accelerators
- To shorten the time of setting or increase the rate of hardening or strength developement.
- eg; Calcium Chloride.
- Uses : (i) Repair work
(iii) Cold Weather
2. Retarders
- To delay the setting of cement.
- eg : Sugar, Carbohydrate derivatives, Soluble zinc salts, gypsum and ignosulphate etc.
- Used in hot weather also.
- To increase workability without increasing the water content.
- Useful for very heavily reinforced sections or where rapid placing of concrete is desired.
- eg; Soda, calcium soaps, vegetable oils, fats, waxes, coal tar, ammonium state, oleate.
4. Air Entraining Agents
- Air to be incorporated in the form of minute bubble in concrete during mixing to increse the workability and resistance to freezing and thawing.
- eg : Vinsol resin, Aluminium powder, Hydrogen peroxide.
**************************All About Mortar****************************
1. What is the mortar ?
---> Mixture used for the joining of bricks.
2.What are the different types of mortar ???
---> There three types of mortar;
(a) Cement Mortar : (cement : sand) 1:3 to 1:8
- Mortar richer than 1:3 should not be used because of high drying shrinkage. Mortars leaner then 1:5 tends to become harsh and unworkable, prone to seggregation. Cement mortars sets early and grain strength quickly.
|
Sr. No |
Types of Woks |
Cement |
Sand |
|
1 |
Masonary |
1 |
4.5 |
|
2 |
Plastering (a) Interior (b) Exterior |
1 1 |
4 5 to 6 |
|
3 |
Pointing |
1 |
1 to 3 |
|
4 |
Reinforcing |
1 |
3 |
|
5 |
Foundation |
1 |
3 to 4 |
(b) Lime Mortar: (lime : sand) 1:2 to 1:3
- Lime mortar gain strength slowly and have low ultimate strength.Lime gives good workability.
(c) Gauged Mortars : (cement : lime : sand) 1:1:6 ; 1:2:9 ; 1:3:12;
- Good workability, free of cracks, rain protection, more water retentivity, gives dense, durable and strong mortar.
***Most of in general case we used the proportion of various mortar in construction industry;
Cement mortar lime mortar
brick masonary 1:6 1:2
plastering 1:4 1:2
grouting and carveneous rock 1:1.5
guniting 1:3
and used 1:3 proportion while in testing of compressive strength of cement.
****GROUT****
- Cement mortar of fluid consistently used to fill the voids and joints in masonary and to repair the cracks.
- In dams: To fill cracks formed after the concrete sets and hardens.
- In tunnel: To fill space between the tunnel walls and surrounding earth.
- In order to increse the workability at low water cement ratio, water reducing admixture such as fly ash, bentonite clay, diatomaceous earth etc. are used
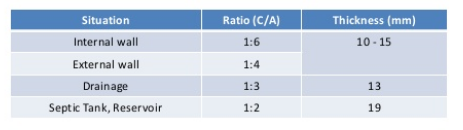
********CEMENT PLASTER*******
- First coat or rough coat is 12 mm average thickness on brick masonary.
- Mix proportion 1:3 or 1:4 .
- Second coat is laid in a thin layer of 3 mm thickness.
mostly in brick masonary wall (shown picture)
**********POINTING**********
- Art of finishing the mortar joints in exposed bricks or stone masonary in order to protect the joints from weather effects and to improve the appearance.
- Mix proportion ( C : FA ) 1:2 or 1:3.
It will Contd in part III....











Comments
Post a Comment